
ENCOURAGING YOUNG PEOPLE TO MAKE INFORMED REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH CHOICES
Contraception

Contraception to delay first pregnancy
There are several methods of contraception that can be used for the prevention and delay of pregnancy.
- Oral Contraceptive Pills
- Injectables
- Emergency Contraception
Other methods such as IUD’s cannot be used as yet.
Post abortion and Post-partum contraception – Myths and Misconceptions
Post abortion contraception
These methods that are available, as options to a woman should be given after considering the patient’s preferences and medical history, anatomic and hormonal factors, and whether or not the woman is breastfeeding.
The term abortion can include the following
- Miscarriage
- Pregnancy termination
Several situations to keep in mind are
- Contraceptive need after abortion
- Contraception after uncomplicated or complicated abortion
- Counseling of clients who have had an abortion
Women who want to avoid pregnancy after induced or spontaneous abortion have the same contraceptive method options and these methods are safe when administered in a proper health care setting by a trained provider.
Some Myths and Facts about POST ABORTION
-Does not substitute other foods for breast milk and is exclusively breastfeeding the baby
-Feeds the baby at least every four hours during the day and every six hours at night
-Has not had a period since she delivered the baby
For breast-feeding women, contraceptive methods can be organized into a three categories
1) Non-hormonal methods that do not interfere with lactation
Breastfeeding is a fairly reliable from of contraception (lactation amenorrhea or LAM). Other non-hormonal methods are barrier methods (male and female condoms), spermicidal and non-hormonal IUD’s. Tubal ligation is also a method that can be included in the non-hormonal methods.
2) Progestin-only hormonal methods
(This may decrease breast milk supply and should therefore be discontinued if that happens), the mini-pill, monthly progesterone shots (DEPO-PROVERA) and progesterone only releasing vaginal rings and implants. Progesterone-only contraceptives are deemed safe for breastfeeding. Some women may experience a decline in breast milk production and should consult their doctor for a change in contraception.
3) Hormonal methods that have estrogen
Breast milk production. These methods include combination oral contraceptive pills, combined injectables and some vaginal rings that have both estrogen and progesterone. As estrogen will affect breast milk production, women should wait till at least 6 months after the birth of their child to start this type of method so the child is breastfed till that time and has progressed onto solids.
As mentioned, all women should avoid the combined estrogen-progestin methods for at least three weeks postpartum to avoid elevating the risk of blood clots, which can be dangerous and fatal.
Virginity – Excess or no bleeding on wedding night
The state of never having engaged in sexual intercourse is called virginity. In our culture, virginity is viewed positively and it is expected that a woman will be a virgin on her wedding night (unless, it is her second marriage or she is divorced).
This expectation comes with a lot of pressure on the woman. Some women are aware and some are unaware with regards to what virginity entails anatomically (bodily structure of a female) and thus the concept of “bleeding” or “spotting” on the night of the wedding.
Let us discuss the anatomy briefly
The female vagina is covered by a thin piece of tissue or “membrane” called the hymen that partially covers the opening to the vagina. Since a girls starts menstruating at the onset of puberty, there has to be a way for the menstrual fluid, or period, to exit the body.
Therefore, the hymen usually does not cover the entire vaginal opening.It is important to note that some women may be born without this membrane and may never have it, while in others it can vary in shape and size. Also, the hymen is lost in some women through physical activities such as bike riding, gymnastics and horse riding.
When a woman engages in sexual intercourse for the first time in her life, described as “penetration of the vagina by the penis”, the hymen is stretched open, and this may or not be painful. At times, tearing or bleeding may occur, however, this manifestation has to do with how flexible the hymen tissue is. Therefore, bleeding may or may not occur on the wedding night, despite the fact that the woman is a virgin.
If bleeding does occur if the bleeding is minimal and there is no pain, then one can continue with intercourse depending on how the woman feels. If there is pain and discomfort, then discontinue intercourse till the pain stops and the woman is comfortable enough to engage in sexual intercourse again.
If bleeding does not occur It is important to note that the absence of bleeding on the wedding night does not in any way mean that the woman is not a virgin. There are a number of women who do not bleed at all and they have previously never engaged in sexual intercourse. As described earlier, some women may have ruptured or lost their hymen earlier while engaging in heavy physical activity, biking, or gymnastics.
The presence of the hymen, as a result of the cultural implications of virginity in our society, is wrongly misconstrued as physical evidence of purity. Purity of character is more than the presence or absence of a hymen and that has to be impressed upon.
Sexual relations between loving couples are meant to be satisfying and enjoyable and may lead to having children and building a family. Sex also needs to be safe. Safe sex means protecting yourself and your partner from sexually transmitted diseases, spacing births or delaying the first birth.
How do I choose the right contraception?
When it comes to contraception, it’s important to use what’s right for you. This will change as you go through life. It is important that you are certain that you are NOT pregnant and wait till your next menstrual period before starting a family planning method in consultation with a doctor.
Find out more about the types of contraception available in Pakistan.
Emergency, Short Term, Medium Term, Long Term, Permanent, Natural.
EMERGENCY CONTRACEPTION
Emergency contraception is used to prevent pregnancy after having unprotected sex and you think there might be a high chance of becoming pregnant. It does not protect against Sexually Transmitted Diseases, only Condom does!
Emergency Contraception can be easily purchased from a local Pharmacy. Contact the toll free number 0800 22 333 for counseling and alternative options or email our panel specialist and get an answer within 24 hours.
Drop a line to :onlinedr@srhmatters.org
The different kinds of emergency contraception options are listed below.
Emergency Contraceptive Pills (ECP)
- Commonly available ECPs in Pakistan are the Progestin Only Emergency Contraceptive Pills.
- These Emergency Contraceptive Pills (ECP) should be taken within 120 hours (5 days) by the female after having unprotected sex to prevent an unwanted pregnancy.
- ECPs are less effective if fertilization has already occurred.
- If the female is pregnant, an ECP will not interrupt the pregnancy but can be dangerous instead.
- About 8 to 10 in every 100 females in a year, who use ECPs can become pregnant despite taking ECPs within 120 hours of having unprotected sex.
- If the 2 pills formulation is taken, the first pill should be taken as soon as possible within 5 days of unprotected intercourse with the second one 12 hours later.
- It is most effective if taken as soon as possible after having unprotected sex. The name ‘morning-after pill’ is somewhat misleading as ideally the pill should be taken immediately after sex, without waiting for the next morning.
- It does not provide protection against Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs).
- Couples having sex must always use a condom to protect themselves against STDs even if they are using another method of birth control.
- A larger-than-normal dose of hormone may cause some side effects in many of the females who take emergency contraception pills; e.g. nausea, vomiting, breast tenderness, and headaches. Such side effects are usually insignificant and most improve within 1 to 2 days.
- The Menstrual Cycle may become temporarily irregular after taking ECPs.
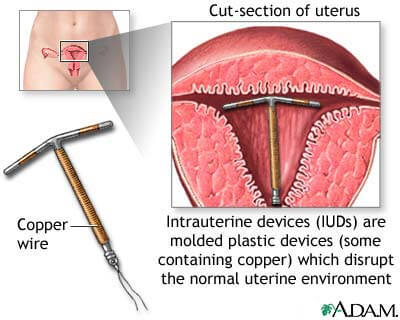
INTRAUTERINE DEVICE (IUD)
- An IUD that is placed in the uterus within 5 days of having unprotected sex can also be used as emergency contraception. It is very safe and widely used all over the world.
- An IUD is a small device that can be left in the body for 5 to 10 years. It will prevent pregnancy during that time.
- Unlike the ECP, an IUD prevents fertilization rather than implantation so it’s not an early abortifacient .It destroys sperm as copper is released to a uterine environment which is hostile for the sperm.
- Emergency IUD insertion is also very effective. It can reduce the risk of pregnancy by 97-99% if inserted within 5 days of unprotected sex.
- A possible side effect of an IUD is bleeding between the Menstrual Cycles.
Hormonal IUCD (Mirena)
Overview:
Mirena is a hormonal intrauterine device (IUD) that can provide long-term birth control (contraception).
The device is a T-shaped plastic frame that’s inserted into the uterus, where it releases a type of the hormone progestin. To prevent pregnancy, Mirena:
- Thickens mucus in the cervix to stop sperm from reaching or fertilizing an egg.
- Thins the lining of the uterus and partially suppresses ovulation.
Mirena prevents pregnancy for up to five years after insertion.
Why it’s done:
Mirena offers effective, long-term contraception. It can be used in premenopausal women of all ages, including teenagers.
Among various benefits, Mirena:
- Eliminates the need to interrupt sex for contraception
- Doesn’t require partner participation
- Can remain in place for up to five years
- Can be removed at any time, followed by a quick return to your normal fertility
- Can be used while breast-feeding — although your health care provider will likely recommend waiting six to eight weeks after childbirth because earlier placement increases the risk of injuring the uterus during placement
- Doesn’t carry the risk of side effects related to birth control methods containing estrogen
Mirena can decrease menstrual bleeding after three or more months of use. About 20 percent of women stop having periods after one year of using Mirena.
Mirena can also decrease:
- Severe menstrual pain and pain related to the abnormal growth of uterine-lining tissue outside the uterus (endometriosis)
- The risk of pelvic infection
- The risk of endometrial cancer
Because of these noncontraceptive benefits, Mirena is often prescribed for women with:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Cramping or pain with periods
- Endometriosis
- Abnormal growth of the lining of the uterus (endometrial hyperplasia)
- Abnormal growth of uterine-lining tissue into the muscular wall of the uterus (adenomyosis)
- Anemia
- Fibroids
Mirena isn’t appropriate for everyone. Your health care provider may discourage use of Mirena if you have:
- Breast cancer, or have had it
- Uterine or cervical cancer
- Liver disease
- Uterine abnormalities, such as fibroids, that interfere with the placement or retention of Mirena
- A pelvic infection or current pelvic inflammatory disease
- Unexplained vaginal bleeding
Tell your health care provider if you:
- Take any medications, including nonprescription and herbal products
- Have diabetes or high blood pressure
- Have a heart condition or have had a heart attack
- Have migraines
- Have blood-clotting problems or have had a stroke
- Recently gave birth or are breast-feeding
Risks
Less than 1 percent of women who use Mirena will get pregnant in a year of typical use.
If you do conceive while using Mirena, you’re at higher risk of an ectopic pregnancy — when the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, usually in a fallopian tube. However, because Mirena prevents most pregnancies, women who use it are at lower risk of having an ectopic pregnancy than are other sexually active women who are not using contraception.
Mirena is generally safe. But it’s important to remember that:
- Headache
- Acne
- Breast tenderness
- Irregular bleeding, which can improve after six months of use
- Mood changes
- Cramping or pelvic pain
It’s also possible to expel Mirena from your uterus. You may be more likely to expel Mirena if you:
- Have never been pregnant
- Have heavy or prolonged periods
- Have severe menstrual pain
- Previously expelled an IUD
- Are younger than age 20
- Had Mirena inserted immediately after childbirth
Your health care provider may recommend removal of Mirena if you develop:
- A pelvic infection
- Inflammation of the endometrium (endometritis)
- Endometrial or cervical cancer
- Pelvic pain or pain during sex
- Very severe migraine
- A significant increase in blood pressure, or have a stroke or heart attack
- Possible exposure to an STI
How you prepare
Your health care provider will evaluate your overall health and do a pelvic exam before inserting Mirena. You may be screened for STIs.
Mirena can be inserted:
- Anytime during your menstrual cycle if you’re not pregnant. You might need to take a pregnancy test to confirm you’re not pregnant.
- Immediately after a pregnancy termination.
- Immediately after delivering a baby vaginally or by cesarean section — although insertion immediately after vaginal delivery increases the risk of expelling Mirena.
If you have Mirena inserted more than seven days after the start of your period, be sure to use backup contraception for one week.
Taking a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medication, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others), one to two hours before the procedure can help reduce cramping.
What you can expect
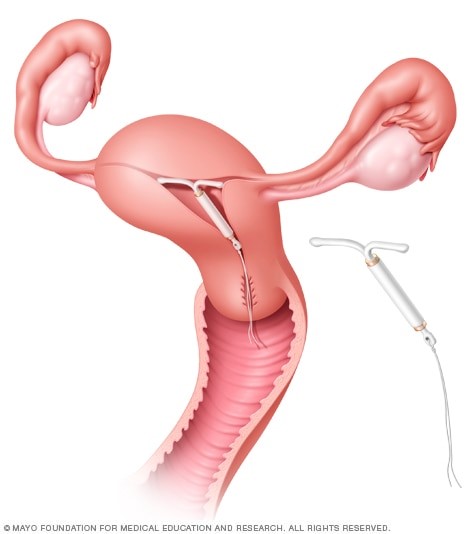
Mirena is typically inserted in a health care provider’s office.
During the procedure
Your health care provider will insert a speculum into your vagina and clean your vagina and cervix with an antiseptic solution. Special instruments might be used to gently align your cervical canal and uterine cavity and to measure the depth of your uterine cavity.
Next, your health care provider will fold Mirena’s horizontal arms and place the device inside an applicator tube. The tube is inserted into your cervical canal, and Mirena is carefully placed in your uterus. When the applicator tube is removed, Mirena will remain in place.
Your health care provider will trim Mirena’s strings so that they don’t protrude too far into the vagina, and may record the length of the strings.
During Mirena insertion, you may experience cramping, dizziness, fainting or a slower than normal heart rate.
After the procedure
Once a month, check to feel that Mirena’s strings are protruding from your cervix. Be careful not to pull on the strings.
About a month after Mirena is inserted, your health care provider may re-examine you to make sure Mirena hasn’t moved and to check for signs and symptoms of infection.
While you’re using Mirena, contact your health care provider immediately if you:
- Think you may be pregnant
- Have unusually heavy, persistent vaginal bleeding
- Have abdominal pain or pain during sex
- Have an unexplained fever
- Have unusual or foul-smelling vaginal discharge, lesions or sores
- Develop very severe headaches or migraines
- Have yellowing of the skin or eyes
- Were exposed to an STI
- Can no longer feel the IUD strings, or they suddenly seem longer
It’s also important to contact your health care provider immediately if you think Mirena is no longer in place. Your provider will check the location of Mirena and, if it’s displaced, remove it if necessary.
Removal
Mirena can remain in place for up to five years. To remove Mirena, your health care provider will likely use forceps to grasp the device’s strings and gently pull. The device’s arms will fold upward as it’s withdrawn from the uterus.
Light bleeding and cramping is common during removal. Rarely, removal can be more complicated.
https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/mirena/about/pac-20391354
E-mail the Panel Specialist to find out more about how IUD’s work. Or call the Toll Free number 0800 22 333 to get more information.
Drop a line to: onlinedr@srhmatters.org
Short Term Contraception
The Combined Pill
This pill contains Oestrogen and Progesterone and is taken by the female. This also prevents the egg from being produced.
Advantages:
The Pill provides protection against cancers of the womb and ovaries and also helps prevent Osteoporosis. It regulates the period and helps reduce PMS (Premenstrual Stress Syndrome). It does not have any long-term effects, and unlike condoms, does not interrupt sex. It can be taken from 6 weeks after giving birth if the mother is not breast feeding.
Disadvantages
Early symptoms of pregnancy may be experienced by some for a few weeks .This can be avoided by taking the pill after meals and at bed time. Other side effects may include headaches, water retention, nausea, weight gain and depression for some.
This is not the recommended option for smokers, women over thirty five, diabetic or high blood pressure patients. Also, after 6 months, if one is breastfeeding, the hormones could pass on to the baby through the milk and milk flow may also be reduced. It does not protect against Sexually Transmitted Diseases, only Condoms do!
Effectiveness:
Over 99% effective if used according to instructions. Less than 1 woman in 100 will get pregnant in a year.
COCPs provide effective contraception from the very first pill if started within five days of the beginning of the menstrual cycle (within five days of the first day of menstruation).
If started at any other time in the menstrual cycle, COCPs provide effective contraception only after 7 consecutive days of use of active pills, so a backup method of contraception such as condoms must be used until active pills have been taken for 7 consecutive days. COCPs should be tried and taken at approximately the same time every day to enhance effectiveness. May not be as effective if taken late or after vomiting or severe diarrhea.
The Mini Pill
This pill is also taken by the female. Consumption of this pill thickens the mucous in the cervix and makes it harder for the sperm to enter the uterus.
Advantages:
This pill can be taken by women who are smokers, over 40, overweight, suffering from high blood pressure, and breastfeeding.
Disadvantages
It has to be taken at the same time each day, and there is a small risk that if you are breastfeeding, the progesterone could harm the baby. It does not protect against Sexually Transmitted Diseases, only Condom does!
Effectiveness
99% effective if taken according to instructions. 1 woman in 100 will get pregnant in a year.
It needs to be taken at the same time each day. Not effective if taken over 3 hours late or after vomiting or severe diarrhea.
Condoms
How to Use

Psychological Problems

Advantages

Mistakes
Advantages
Condoms are easy to use with minimal health risks and are easily available everywhere. Many of the condoms contain spermicide, which is a substance that kills sperms, therefore preventing a woman from getting pregnant. Condomsensure safe sex. There are various types of condoms available in the market and some are specially designed especially to enhance pleasure during intercourse.
Disadvantages
The biggest disadvantage of condoms is that sexual flow has to be interrupted when the condom has to be worn. Condoms could also slip off or get torn duringintercourse. Another disadvantage is that it has to be removed straight after intercourse. In some cases, condoms may reduce sexual pleasure.
Effectiveness
98% if used according to the following instructions.
Instructions for Putting on a Condom
- Have a condom on hand.
- Make sure the condom isn’t past its expiration date, and has not been tampered with or damaged.
- Carefully tear open condom packet. Do not use scissors, knife or blade.
- Hold tip of condom to create an air-free reservoir for semen.
- Roll condom over the base of the penis.
- Add water-based lubricants only. Oil based lubricants can damage the condom.
- If a condom breaks during intercourse, stop and immediately replace it with a new one.
- Hold condom at the base during withdrawal from intercourse.
- Dispose off condom in trash.
- Never flush condoms down the toilet.
Medium Term
Injections
Females can take injections to prevent possible pregnancies. The injection given every 2-3 months contains progesterone which prevents an egg from being produced.
Advantages
People with diabetes and high blood pressure can use these safely. It is a long lasting method of contraception.
Disadvantages
Slight Weight gain may be experienced after one year of use, nausea, and irregular bleeding can all be side effects. Fertility may also take a couple of months to return. It does not protect against Sexually Transmitted Diseases, only Condom does!
Effectiveness
99.7%
Long Term
Intrauterine Device
(IUD). IUD is a small plastic or metal object that is placed inside a woman’s uterusto prevent a sperm from settling there.
Advantages
IUD’s work as soon as they are fitted, and have no effect on breastfeeding or on one’s hormones. They are inserted by a doctor/trained service provider and can prevent a pregnancy from occurring for up to 5 years.
Disadvantages
Sometimes, IUD’s can result in heavy period flow and uterine cramping. It does not protect against Sexually Transmitted Diseases, only Condom does!
Effectiveness
Around 99% effective.
Reversibility
Possible
Implant (Norplant)
It is a flexible tube put under the skin of the arm. It releases the hormone progestogen. It stops ovulation, thickens cervical mucus to prevent sperm meeting an egg and thins the lining of the womb to prevent an egg implanting.
Advantages
Works for three years but can be taken out at any time. You don’t have to think about contraception for as long as the implant works. When the implant is removed, the normal level of fertility returns.
Disadvantages
Periods are often irregular, much longer or stop completely for at least the first year. Some women gain weight. Other possible side-effects include headaches, spotty skin, mood changes and breast tenderness.
Effectiveness
Over 99% effective. Some medicines may stop the implant from working so make sure that whenever you visit any doctor, he knows that you have the implant in place.
Reversibility
Possible, provided correctly inserted.
Permanent Contraception
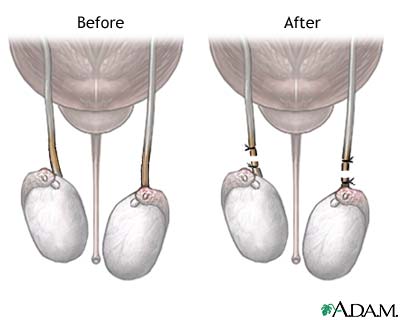
For Males
Reversibility
Possible, but expensive and low success rate.
Male sterilization or vasectomy is a medical procedure, whereby parts of the tubes that carry sperm are ligated and cut. This prevents the man from making the woman pregnant. Vasectomy does not involve the removal of the testicles and it affects neither the production of male sex hormones (mainly testosterone), thus it does not decrease libido nor their secretion into the bloodstream. Vasectomy does not protect against Sexually Transmitted Diseases, only Condom does!
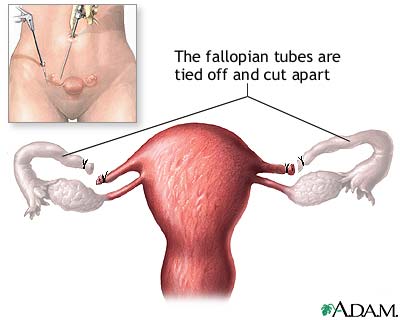
For Females:
Reversibility
Sometimes possible. Female sterilization is done by blocking the fallopian tubes. It is also called tubal ligation. Both types of sterilization are effectively irreversible. Neither has an effect on a man or woman’s ability to have or enjoy sex. Sterilization does not protect against Sexually Transmitted Diseases, only Condom do!
Natural Methods
Rhythm Method or Fertility awareness
Ovulation occurs in the mid cycle days before a period, so one has to have a regular menstrual cycle in order to accurately predict a ‘safe’ time for intercourse.
Advantages
There are no side effects for this natural form of birth control.
Disadvantages
There are restrictions on sex, which could lead to a strain on the relationship of the couple. Furthermore, if one does not have a regular menstrual cycle, miscalculation of dates can occur, resulting in not knowing what a ‘safe’ time forintercourse is.
By the rhythm method, a simple way to calculate the time you are most fertile is described below:
Monitor your cycle for 6 months to calculate the duration of your periods
The first day is counted as Day 1 Subtract 18 from the day of your shortest recorded cycle – this will tell you the estimated first day of your fertile time Subtract 11 from the length of your longest recorded cycle – this will tell you the last day of your fertile time.
During the fertile stage the couple can avoid sex, or use the barrier or withdrawal method in order to avoid a possible pregnancy.
Abstinence
Abstinence is when the couple refrains from having sexual intercourse. This is usually at the time when the woman is ovulating. Abstinence requires discipline and is usually not a very reliable method of contraception.
Withdrawal
Also referred to as “pulling out,” is when the man removes his penis from the woman’s body before he ejaculates. Withdrawal is not a good method for men who cannot accurately tell when they are about to ejaculate or “come”.
However, practicing withdrawal is a little bit more effective than using no method at all, but in the presence of more reliable methods of birth control, it is not a very dependable method.
Withdrawal is not an effective way of avoiding STD’s, the only effective way to avoid STD’s is to use condoms..
The National Health Service in the UK has produced some good patient-targeted information about the risks and benefits of taking the pill. Please click on the link below for information.
If you want more information about cancer and the pill, the Cancer Research UK website has a good summary of the research evidence. For details please click on the link below.
